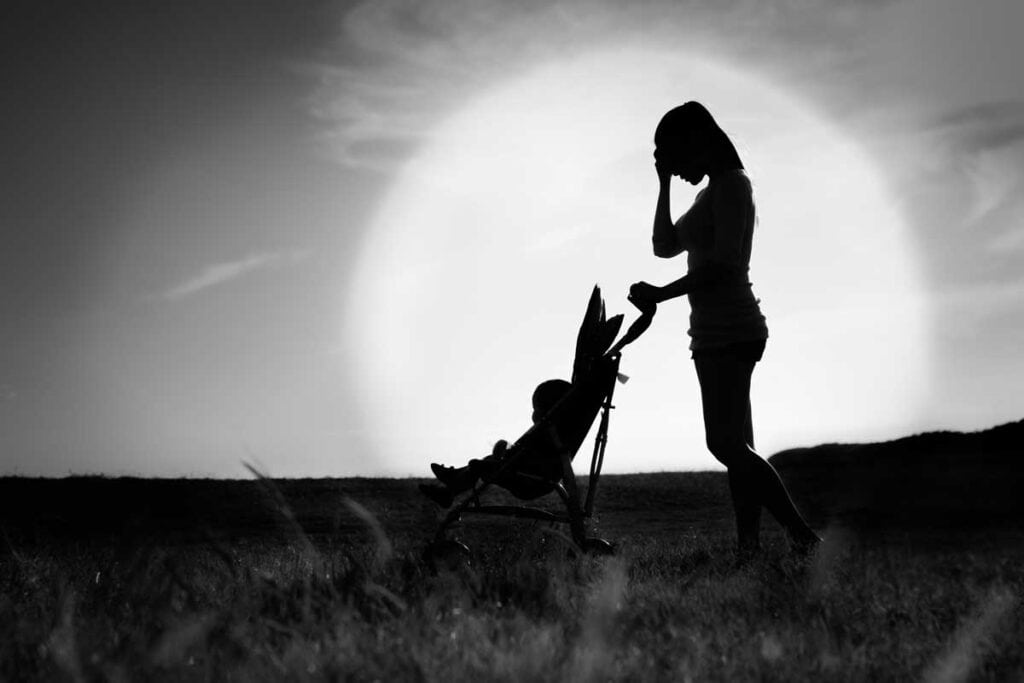
If worry and fear have become overwhelming companions since having your baby, you might be facing postpartum anxiety. Not uncommon among new parents, this condition can make it hard to relax, disrupt your sleep, and challenge your daily routines. Recognizing its signs is the first step towards managing it effectively. This article offers insight into what postpartum anxiety looks like, why it happens, and how to seek relief, giving you the tools to regain control and enjoy parenthood.
Key Takeaways
-
Postpartum anxiety is a serious condition affecting approximately 15-20% of new mothers, manifesting as persistent, irrational fears that go beyond typical parental concerns, and can impair a mother’s daily functioning and childcare.
-
Postpartum anxiety has both physical symptoms (such as dizziness, hot flashes, and nausea) and psychological impacts (like severe mood swings and persistent worry), which are exacerbated by factors like hormonal changes and stressful life events.
-
Treatment options for postpartum anxiety include therapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustments; early recognition and professional intervention are crucial, and supportive environments and self-care strategies can also play a significant role in managing the condition.
Unveiling Postpartum Anxiety: What It Really Is
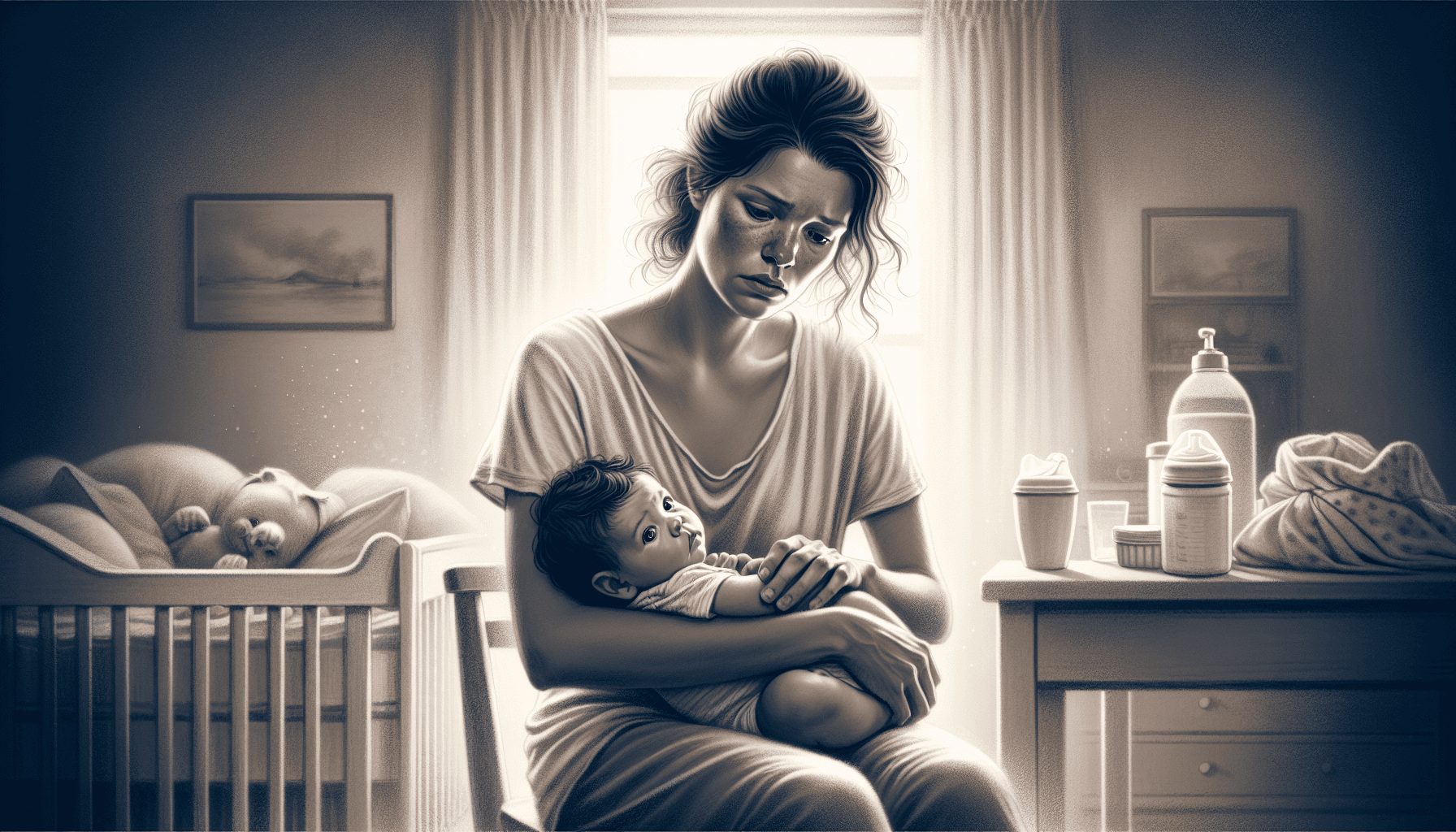

Imagine yourself as a fresh mother, your newborn in your arms. The warmth and affection you feel are immense, but concurrently, an unexplainable worry eats away at you. This anxiety is relentless—a persistent dread that cloaks all other emotions. It’s possible this isn’t merely the standard fretting of first-time parenthood. It might be postpartum anxiety, which afflicts about 15 to 20% of new mothers. Though it can be just as crippling as postpartum depression, it often remains under the radar.
This type of anxiety may share ties with generalized anxiety disorder and manifests through:
-
Constant fears that lack rationality
-
Concerns extending well beyond those commonly held by mothers
-
An incessant sense of doom
-
Consuming worries over potential misfortunes
-
Fears not necessarily rooted in actual issues or dangers
Defining the Disorder
Anxiety disorder in the form of postnatal anxiety is characterized by extreme apprehension or dread that can hinder a new mother’s self-care and her capacity to nurture her infant. This intense anxiety goes beyond common concerns held by new parents, stemming from irrational or overstated fears.
Far more critical than just experiencing ‘baby blues,’ this disorder greatly hampers one’s daily life activities. It could compromise a mother’s ability to conduct routine duties and partake in essential childcare practices, which might influence the connection between mother and baby as well as potentially harm the child’s well-being.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Embarking on the path to assistance starts with identifying symptoms of postpartum anxiety, which can encompass:
-
A constant state of tension and an incapacity to unwind
-
Ongoing apprehension or dread about potential misfortunes
-
Sleep disturbances
-
Reduced interest in eating
-
An inability to remain still
-
Physical indicators like lightheadedness or feelings of sickness
Should you find yourself experiencing any of the above signs, it’s critical that you seek help.
At times, this form of anxiety could take shape as obsessive-compulsive disorder during the postpartum period. This includes continuous intrusive thoughts along with repetitive actions centered around concerns for your newborn’s well-being.
Understanding the Onset
The critical phase for the onset of postpartum anxiety typically falls within the first several weeks following childbirth, making the immediate postpartum period a time of particular concern. Early recognition is essential as symptoms can quickly intensify if not identified during this initial stage.
Factors like past mental health challenges, the pressures associated with giving birth, and lack of sleep are known to potentially provoke an episode of postpartum anxiety right after delivery.
The Physical Manifestations of Postpartum Anxiety
Our bodies often mirror the condition of our minds, and this is especially evident in how physical symptoms can signal severe anxiety. Those enduring postpartum anxiety might experience an array of bodily signs including dizziness, nausea, and hot flashes. These are tangible indicators that reveal the body’s response to the stress caused by anxiety symptoms, serving as an alert that there is a problem needing attention.
Bodily Reactions
New mothers grappling with postpartum anxiety may face substantial obstacles in their daily lives due to the real physical symptoms and discomforts it can cause. Panic attacks can lead to experiencing heart palpitations and sensations of chest pain that, while extremely distressing, are not indicative of any physical danger.
Individuals dealing with this form of anxiety might encounter feelings similar to being submerged underwater. A tightness in the chest accompanied by profound fatigue is characteristic during these episodes.
Hormonal Influences
Hormonal fluctuations following childbirth, particularly the sharp decrease in estrogen and progesterone levels, can impact mood during the postpartum period. This change may interfere with brain chemicals such as serotonin that regulate mood, potentially triggering symptoms associated with postpartum anxiety due to each person’s unique response to these hormonal shifts.
Imbalances in thyroid function also present a risk factor for developing anxiety symptoms in the postpartum phase. These findings suggest that various hormonal changes are implicated in how anxiety manifests after giving birth.
The Psychological Impact: Emotional Trauma and Stress
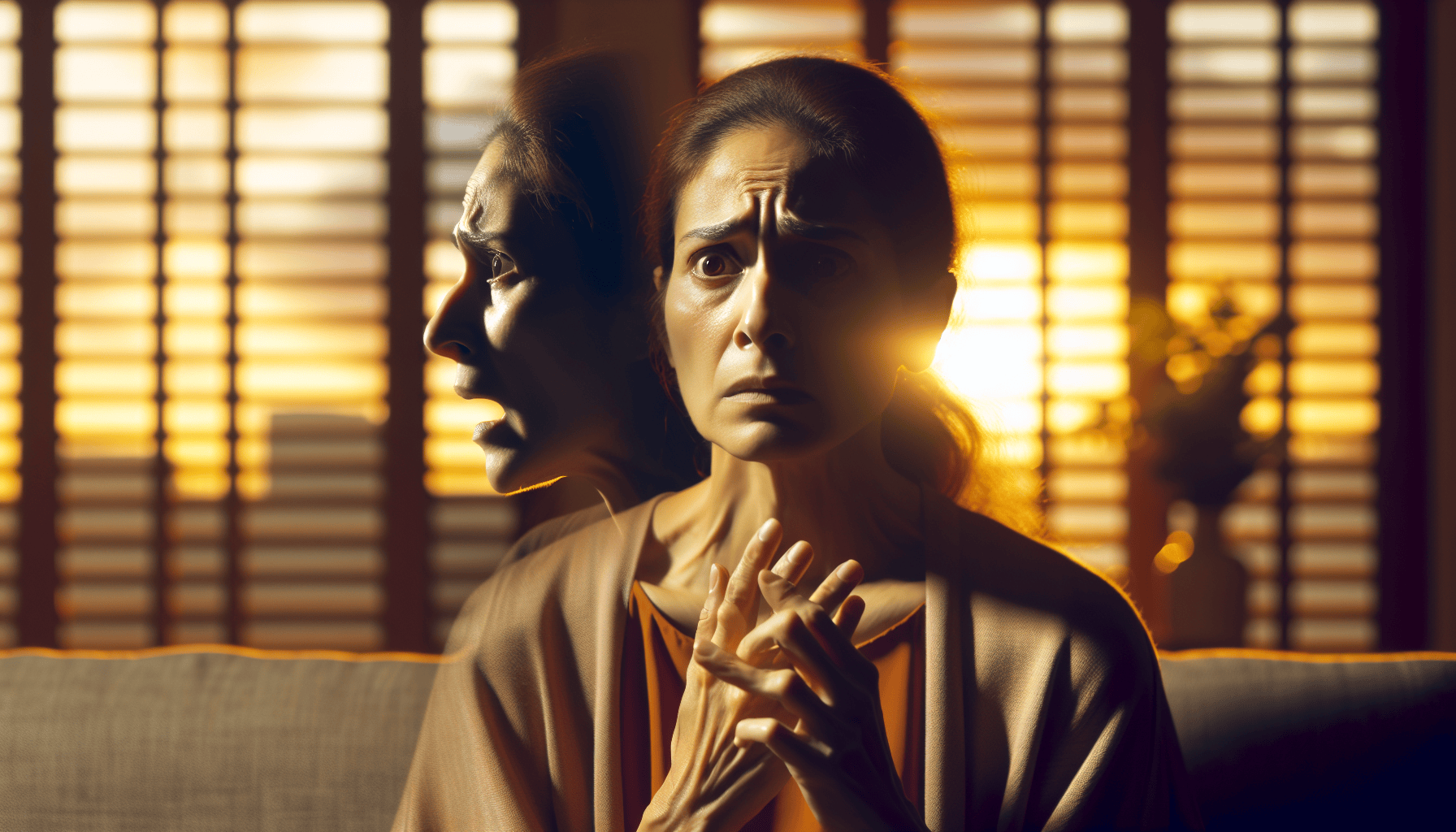

In the realm of mental health, postpartum anxiety presents itself through a series of symptoms:
-
A state of generalized anxiety is marked by ongoing, excessive worries that disrupt an individual’s capacity to unwind and typically center around concerns for the infant’s well-being and safety.
-
Intense fluctuations in mood
-
Experiences of melancholy
-
A sensation of agitation
-
Despondency
-
Challenges with maintaining focus
-
Continual somatic complaints such as migraines or gastrointestinal distress
These manifestations intensify the psychological toll taken by postpartum anxiety.
Navigating Emotional Turbulence
Managing the turbulent emotional landscape is a frequent challenge for new mothers grappling with postpartum anxiety and issues related to maternal mental health. A pervasive fear that something terrible might occur often engulfs them, accompanied by physical manifestations like relentless thoughts, disruptions in sleep patterns, and appetite fluctuations.
Occasionally, as observed with postpartum OCD, these new mothers may engage in evasive tactics by shunning tasks such as bathing or holding their infant because of intense compulsive urges.
Stressful Life Events
Challenging conditions can substantially elevate stress and anxiety levels in women who have recently given birth. These conditions include:
-
the experience of a difficult childbirth
-
the process of recovering from giving birth
-
complications with breastfeeding
-
adjusting to life as a new mother
Anxiety after giving birth may be enduring or might reappear when faced with stresses related to child care, suggesting that this issue doesn’t always dissipate naturally and could represent an ongoing concern.
Experiencing traumatic events during childbirth, such as unexpected cesarean sections or interventions like vacuum extraction or forceps use, may give rise to postpartum PTSD. This type of anxiety is characterized by intense fear and continuous trauma-related stress.
Risk Factors and Identifying Mothers at Risk
Understanding the risk factors for postpartum anxiety is crucial in identifying mothers who may be at risk. Risk factors include stressful events during or after pregnancy, medical issues faced during childbirth, ambivalent emotions about being pregnant, and a deficit of robust emotional support networks. Notably, experiencing state anxiety early in the postpartum period can serve as a strong indicator of later postpartum anxiety. Additional elements like employment status, prior experiences with depression, and unplanned pregnancy also play roles.
Certain obstetric details are linked to heightened risks for developing postpartum anxiety: these include past induced abortions and specific delivery methods such as cesarean sections or instrumental vaginal births. Previous encounters with significant reproductive challenges like miscarriages coupled with earlier instances of either general anxieties or panic attacks before conception or while pregnant could increase vulnerability to this condition during the postnatal phase.
Personal and Family History
Having a history of anxiety disorders or affective disorders within one’s personal or family background plays a crucial role in elevating the risk of experiencing postpartum anxiety. Research indicates that 9.2% of those who suffer from postpartum anxiety also have relatives with psychiatric disorder histories.
It is more common for women who have personally dealt with depression to face challenges related to postpartum anxiety.
Other Contributing Factors
Aside from individual and family history, additional elements can play a role in the onset of postpartum anxiety. Among them are:
-
A background of depression or anxiety that correlates with a higher likelihood of facing postpartum anxiety
-
Instances of antenatal anxiety throughout pregnancy
-
Prior instances of pregnancy loss, which could lead to increased levels of anxiety following the birth
Acknowledging these factors is critical for properly evaluating and handling cases involving postpartum anxiety.
Treatment Pathways for Postpartum Anxiety
Treatment for postpartum anxiety varies based on the intensity of the symptoms and can include:
-
Psychological counseling
-
Pharmacotherapy
-
Personal care practices
-
Encouragement from family and friends
Immediate intervention is critical to overcome postpartum anxiety, which does not improve without help.
A multitude of methods effectively address postpartum anxiety. The therapeutic approach may involve modifications in daily activities, psychological support, or prescribed drugs depending on what suits best for the person concerned.
Professional Interventions
Professional guidance is critical in the management of postpartum anxiety. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) often takes center stage, helping new mothers by identifying and transforming unhelpful thinking patterns along with their reactions to stress. For pharmaceutical intervention, Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly administered as they play a vital role in boosting serotonin levels that contribute to mood stabilization.
When it comes to medication like SSRIs for treating postpartum anxiety, choices are made with great caution, especially for breastfeeding women to ensure the safety of the baby. CBT strategies may be enhanced through involving partners, which can bolster communication and expand support networks while ensuring care plans are tailored based on individual health histories and specific needs of each mother.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Support Systems
Making lifestyle changes and having a solid support network are crucial for managing postpartum anxiety alongside professional help. Lifestyle recommendations include practicing yoga, consuming a nutritious diet, and prioritizing sleep to alleviate symptoms of anxiety. Engaging in regular physical activity is recognized as an effective way to decrease anxiety levels and boost mental wellness following childbirth. The assistance from family or friends with household tasks or caring for the baby can offer invaluable emotional support that lightens the load for new parents.
Flexible work arrangements also make it easier for new mothers and fathers to juggle their personal lives with professional responsibilities, which can diminish stress while increasing job contentment. Participating in groups designed for newly minted parents offers camaraderie and mutual understanding that might reduce anxious feelings. SAMHSA’s National Helpline along with other dedicated helplines provide round-the-clock confidential assistance including counsel and connection to local resources such as treatment centers or supportive communities.
Special Cases: Postpartum OCD and Psychosis

Postpartum anxiety is a common issue that can intensify into specific conditions such as Postpartum OCD and Psychosis, necessitating specialized care. New mothers may develop postpartum OCD, an anxiety disorder marked by persistent and intrusive thoughts about their infants that are both irrational and distressing. This condition predominantly targets new moms who might not seek help due to feelings of shame or the fear of having their child removed.
These obsessive thoughts occur with much greater frequency in mothers suffering from postpartum OCD—they’re up to five times more likely than others to have these experiences—but they often keep this hidden for fear of being misunderstood or institutionalized. Fortunately, treating symptoms effectively is possible through medications and cognitive behavioral therapy tailored specifically for those with postpartum OCD.
Obsessive Compulsive Tendencies
New mothers often experience unwanted and repetitive obsessional thoughts, known as postpartum OCD. These symptoms typically manifest as fears of inadvertently harming their infant, excessive worry about cleanliness, and concerns over the baby’s safety.
Postpartum women dealing with this condition may engage in compulsive actions such as repeatedly checking on their child, engaging in frequent ritualistic prayers for the baby’s well-being, constantly seeking reassurance from others or carrying out extensive cleaning routines. Such behaviors are frequently prompted by intrusive thoughts that can impede a mother’s capacity to nurture her child effectively without any real desire to cause harm.
Recognizing Postpartum Psychosis
A serious mental health disorder, postpartum psychosis, emerges soon after a woman gives birth, with its symptoms usually manifesting within the first week following delivery. It is imperative to seek urgent medical care when signs of this rare but severe condition are observed, due to the risk of dangerous behaviors associated with it.
Strategies for New Parents: Coping with Anxiety
Navigating the trials of becoming new parents, especially in facing postpartum anxiety, there are efficient approaches to handle this issue.
To mitigate postpartum anxiety, new parents may employ practical tactics without medication. Allocating time for breaks and personal downtime can significantly reduce feelings of anxiety following childbirth.
Self-Care Techniques
Engaging in regular physical exercise serves as a crucial method of self-care, which can significantly mitigate the symptoms associated with postpartum anxiety. New mothers who are facing such challenges will find particular benefits from participating in activities that include:
-
Walking
-
Jogging
-
Cycling
-
Swimming
-
Yoga
-
Meditation
Incorporating strength training and exercises involving resistance into one’s fitness routine has been shown to bolster mental health for individuals struggling with postpartum anxiety.
Building a Supportive Environment
Establishing a nurturing atmosphere can be crucial in helping control postpartum anxiety. New parents can access support groups, often found online, which serve as an avenue for mothers to share their experiences and connect with others facing similar challenges.
Introducing job-sharing options may also offer new parents the ability to divide work duties, granting them enhanced flexibility and more time for personal well-being and family commitments. A workplace supportive of new parents might also include amenities such as on-site childcare facilities that reduce worry by ensuring their children are safely cared for while they attend to their professional responsibilities.
Cultivating a culture where open dialogue is welcomed allows new parents to comfortably discuss the difficulties they face and articulate what help they need—a key element in creating a robust support system.
Summary
To sum up, a substantial proportion of new mothers experience postpartum anxiety, yet it frequently goes unnoticed. Identifying the symptoms is crucial as is being aware of the risk factors and obtaining proper care. It’s important to remember that there are resources at hand for support and you’re not isolated in facing this demanding period.
Your Emotional Doula & Guide to a Healthy Postpartum Recovery
Embark on your postpartum recovery journey with Shayna Givertz, your Emotional Doula and expert guide through the intricate path of new parenthood. If you’re feeling overwhelmed, lost, or simply in need of a compassionate ear, Shayna is here to offer the support and guidance you deserve.
With her personal experience and professional expertise in yoga and postpartum coaching, Shayna provides a unique blend of emotional and physical support tailored to your specific needs. Connect with someone who understands deeply and can help navigate this challenging yet beautiful phase of life.
Take the first step towards a healthier, more joyful postpartum experience. Sign up now for a free 15-minute consultation with Shayna and start transforming your journey today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is postpartum anxiety?
An anxiety disorder that manifests specifically in new mothers is recognized as postpartum anxiety. This condition can lead to overwhelming concerns or fears, which significantly interfere with the mother’s capacity to attend to her own needs or those of her infant.
If one is dealing with these symptoms, it’s crucial to pursue assistance and therapeutic options.
What are the symptoms of postpartum anxiety?
If you’re experiencing postpartum anxiety, you may notice symptoms like persistent worry, disrupted sleep, decreased appetite, and difficulty relaxing or sitting still. Physical symptoms such as dizziness or nausea may also be present.
It’s important to seek support if you recognize these signs.
How is postpartum anxiety treated?
Depending on the intensity of postpartum anxiety, various treatments are available such as medication, therapy, self-help techniques and support from relatives and friends. Seeking expert advice is crucial to identify the most effective treatment for this condition.
What are some self-care strategies for managing postpartum anxiety?
In dealing with postpartum anxiety, it is beneficial to engage in physical exercises such as yoga or taking walks. Ensuring you maintain a nutritious diet and get enough rest are also crucial self-care practices that can greatly assist in controlling anxiety levels.
How can a supportive environment help in managing postpartum anxiety?
Providing an environment that offers emotional support can alleviate the challenges associated with becoming new parents. This includes making resources available such as on-site childcare and facilitating support groups specifically for those experiencing their early stages of parenthood.
Such measures are effective in assisting with the regulation of postpartum anxiety.












